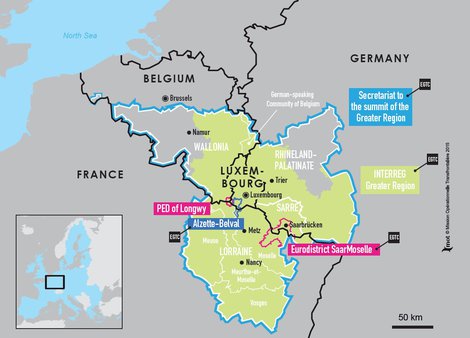
Border: Belgium-Luxembourg
Date(s) of establishment: 1839 - tracé actuel en 1919Length of border: 148 km
Regions concerned: Belgium – Provinces of Luxembourg and Liège
Luxembourg – Ardennes, Luxembourg City, Red Lands (Terres Rouges)
European programme(s):
- Interreg IV A "Grande Région":
The programme on the Inforegio website
The border between Luxembourg and Belgium stretches over 148 km. It begins in the south at the tripoint between the Belgian, Luxembourgish and French borders, and ends in the north at the intersection of the German, Belgian and Luxembourgish borders. The boundary line is noticeably S-shaped and is indicated by 507 border markers, easily recognisable by their points (as in the photograph).
History
In 1831, Belgium obtained its independence from the Netherlands and the London Conference allocated part of the territory of the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg to the new country, thus creating the border. However, at this time, Belgium still held the French-speaking part of Luxembourg as well as the region of Arlon. The German Confederation only wished to include German-speaking regions within its territory.
Following the Treaty of Versailles in 1919, the Belgium-Luxembourg border was redrawn, with Luxembourg recovering the French-speaking province.
Cross-border cooperation
Given their modest size and central position in Europe, Belgium and Luxembourg invested themselves in cross-border cooperation very early on. These two countries do not benefit from a cross-border cooperation programme specifically dedicated to them, but they both participate in the programme for the Greater Region – a very advanced territory in matters of cross-border cooperation.